Bouc-Wen model of hysteresis
In structural engineering, the Bouc-Wen model of hysteresis is used to describe non-linear hysteretic systems. It was introduced by Bouc[1][2] and extended by Wen,[3] who demonstrated its versatility by producing a variety of hysteretic patterns. This model is able to capture, in analytical form, a range of hysteretic cycle shapes matching the behaviour of a wide class of hysteretical systems. Due to its versatility and mathematical tractability, the Bouc-Wen model has gained popularity. It has been extended and applied to a wide variety of engineering problems, including multi-degree-of-freedom (MDOF) systems, buildings, frames, bidirectional and torsional response of hysteretic systems, two- and three-dimensional continua, soil liquefaction and base isolation systems. The Bouc-Wen model, its variants and extensions have been used in structural control—in particular, in the modeling of behaviour of magneto-rheological dampers, base-isolation devices for buildings and other kinds of damping devices. It has also been used in the modelling and analysis of structures built of reinforced concrete, steel, masonry and timber.
Contents |
Model formulation
Consider the equation of motion of a single-degree-of-freedom (sdof) system:
-
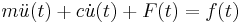
(
here, 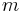 represents the mass,
represents the mass, 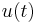 is the displacement,
is the displacement, 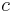 the linear viscous damping coefficient,
the linear viscous damping coefficient, 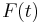 the restoring force and
the restoring force and 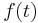 the excitation force while the overdot denotes the derivative with respect to time.
the excitation force while the overdot denotes the derivative with respect to time.
According to the Bouc-Wen model, the restoring force is expressed as:
-
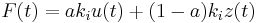
(
where 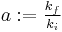 is the ratio of post-yield
is the ratio of post-yield 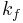 to pre-yield (elastic)
to pre-yield (elastic) 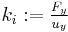 stiffness,
stiffness, 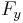 is the yield force,
is the yield force, 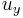 the yield displacement, and
the yield displacement, and 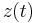 a hysteretic parameter (usually called the hysteretic displacement) that obeys the following nonlinear differential equation with zero initial condition (
a hysteretic parameter (usually called the hysteretic displacement) that obeys the following nonlinear differential equation with zero initial condition (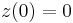 ), and that has dimensions of length:
), and that has dimensions of length:
-
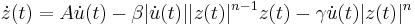
(
or simply as
where 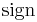 denotes the signum function, and
denotes the signum function, and 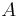 ,
, 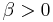 ,
, 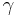 and
and 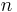 are dimensionless quantities controlling the behaviour of the model (
are dimensionless quantities controlling the behaviour of the model (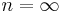 retrieves the elastoplastic hysteresis). Take into account that in the original paper of Wen (1976) [3],
retrieves the elastoplastic hysteresis). Take into account that in the original paper of Wen (1976) [3], 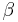 is called
is called 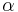 , and
, and 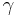 is called
is called 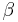 . Nowadays the notation varies from paper to paper and very often the places of
. Nowadays the notation varies from paper to paper and very often the places of 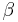 and
and 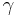 are exchanged; we will stick to the notation used by Ref.[4]. The restoring force
are exchanged; we will stick to the notation used by Ref.[4]. The restoring force 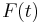 can be decomposed into an elastic and a hysteretic part as follows:
can be decomposed into an elastic and a hysteretic part as follows:
and
therefore, the restoring force can be understood as two springs connected in parallel.
For small values of the positive exponential parameter 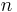 the transition from elastic to the post-elastic branch is smooth, while for large values that transition is abrupt. Parameters
the transition from elastic to the post-elastic branch is smooth, while for large values that transition is abrupt. Parameters 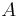 ,
, 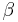 and
and 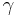 control the size and shape of the hysteretic loop. It has been found that the parameter
control the size and shape of the hysteretic loop. It has been found that the parameter 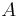 is redundant (Ma et al.(2004) [5]).
is redundant (Ma et al.(2004) [5]).
Wen [3] assumed integer values for 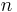 ; however, all real positive values of
; however, all real positive values of 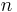 are admissible. The parameter
are admissible. The parameter 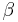 is positive by assumption, while the admissible values for
is positive by assumption, while the admissible values for 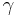 , that is
, that is ![\textstyle \gamma:=[-\beta,\beta]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/13b3439df8a7aaa8ea270676d80be3c0.png) , can be derived from a thermodynamical analysis (Baber and Wen (1981) [6]).
, can be derived from a thermodynamical analysis (Baber and Wen (1981) [6]).
Definitions
Some terms are defined below:
- Softening: Slope of hysteresis loop decreases with displacement
- Hardening: Slope of hysteresis loop increases with displacement
- Pinched hysteresis loops: Thinner loops in the middle than at the ends. Pinching is a sudden loss of stiffness, primarily caused by damage and interaction of structural components under a large deformation. It is caused by closing (or unclosed) cracks and yielding of compression reinforcement before closing the cracks in reinforced concrete members, slipping at bolted joints (in steel construction) and loosening and slipping of the joints caused by previous cyclic loadings in timber structures with dowel-type fasteners (e.g. nails and bolts).
- Stiffness degradation: Progressive loss of lateral stiffness in each loading cycle
- Strength degradation: Degradation of strength when cyclically loaded to the same displacement level. The term "strength degradation" is somewhat misleading, since strength degradation can only be modeled if displacement is the input function.
Absorbed hysteretic energy
Absorbed hysteretic energy represents the energy dissipated by the hysteretic system, and is quantified as the area of the hysteretic force under total displacement; therefore, the absorbed hysteretic energy (per unit of mass) can be quantified as
that is,
here 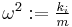 is the squared pseudo-natural frequency of the non-linear system; the units of this energy are
is the squared pseudo-natural frequency of the non-linear system; the units of this energy are 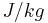 .
.
Energy dissipation is a good measure of cumulative damage under stress reversals; it mirrors the loading history, and parallels the process of damage evolution. In the Bouc-Wen-Baber-Noori model, this energy is used to quantify system degradation.
Modifications
Bouc-Wen-Baber-Noori model
An important modification to the original Bouc-Wen model was suggested by Baber and Wen (1981)[6] and Baber and Noori (1985, 1986).[7][8] This modification included strength, stiffness and pinching degradation effects, by means of suitable degradation functions:
where the parameters 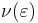 ,
, 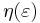 and
and 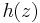 are associated (respectively) with the strength, stiffness and pinching degradation effects. They are defined as linearly-increasing functions of absorbed hysteretic energy
are associated (respectively) with the strength, stiffness and pinching degradation effects. They are defined as linearly-increasing functions of absorbed hysteretic energy 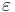 :
:
The pinching function 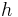 is specified as:
is specified as:
where
and 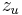 is the ultimate value of
is the ultimate value of 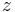 , given by
, given by
Observe that the new parameters included in the model are: 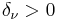 ,
, 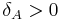 ,
, 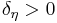 ,
, 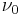 ,
, 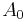 ,
, 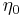 ,
, 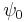 ,
, 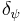 ,
, 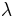 ,
, 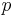 and
and 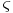 . When
. When 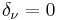 ,
, 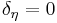 or
or 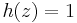 no strength degradation, stiffness degradation or pinching effect is included in the model.
no strength degradation, stiffness degradation or pinching effect is included in the model.
Foliente (1993 [9] and Heine (2001)[10] slightly altered the pinching function in order to model slack systems. An example of a slack system is a wood structure where displacement occurs with stiffness seemingly null, as the bolt of the structure is pressed into the wood.
Two-degree-of-freedom generalization
A two-degree-of-freedom generalization was defined by Park et al. (1986)[11] to represent the behaviour of a system constituted of a single mass 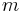 subject to an excitation acting in two orthogonal (perpendicular) directions. For instance, this model is suited to reproduce the geometrically-linear, uncoupled behaviour of a biaxially-loaded, reinforced-concrete column.
subject to an excitation acting in two orthogonal (perpendicular) directions. For instance, this model is suited to reproduce the geometrically-linear, uncoupled behaviour of a biaxially-loaded, reinforced-concrete column.
Wang and Wen modification
Wang and Wen (1998)[12] suggested the following model to account for the asymmetric peak restoring force:
where 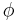 is an additional parameter, to be determined.
is an additional parameter, to be determined.
Asymmetrical hysteresis
Asymmetric hysteretical curves appear due to the asymmetry of the mechanical properties of the tested element, of the imposed cycle motion, or of both. Song and Der Kiureghian (2006)[4] proposed the following function for modelling those asymmetric curves:
where 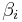 ,
, 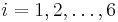 are six parameters that have to be determined in the identification process. However, according to Ikhouane et al. (2008),[13] the coefficients
are six parameters that have to be determined in the identification process. However, according to Ikhouane et al. (2008),[13] the coefficients 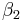 ,
, 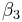 and
and 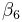 should be set to zero.
should be set to zero.
Calculation of hysteretic response
In displacement-controlled experiments, the time history of the displacement 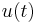 and its derivative
and its derivative 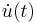 are known; therefore, the calculation of the hysteretic variable and restoring force is performed directly using equations Eq. 2 and Eq. 3.
are known; therefore, the calculation of the hysteretic variable and restoring force is performed directly using equations Eq. 2 and Eq. 3.
In force-controlled experiments, by substituting Eq. 2, Eq. 1 and Eq. 3 they can be transformed in state space form, using the change of variables 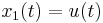 ,
, 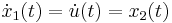 ,
, 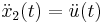 and
and 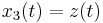 as:
as:
and solved using, for example, the Livermore predictor-corrector method, the Rosenbrock methods or the 4th/5th-order Runge-Kutta method. The latter method is more efficient in terms of computational time; the others are slower, but provide a more accurate answer.
The state-space form of the Bouc-Wen-Baber-Noori model is given by:
This is a stiff ordinary differential equation that can be solved, for example, using the function ode15 of MATLAB.
According to Heine (2001),[10] computing time to solve the model and numeric noise is greatly reduced if both force and displacement are the same order of magnitude; for instance, the units kN and mm are good choices.
Parameter constraints and identification
The parameters of the Bouc-Wen model have the following bounds 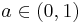 ,
, 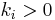 ,
, 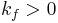 ,
, 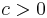 ,
, 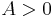 ,
, 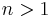 ,
, 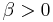 ,
, ![\textstyle \gamma\in[-\beta,\beta]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/26780b64010c307993c63e6ed47187d1.png) .
.
Ma et al.(2004)[5] proved that the parameters of the Bouc-Wen model are functionally redundant; that is, there exist multiple parameter vectors that produce an identical response from a given excitation. Removing this redundancy is best achieved by setting 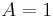 .
.
Constantinou and Adnane (1987)[14] suggested imposing the constraint 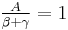 in order to reduce the model to a formulation with well-defined properties.
in order to reduce the model to a formulation with well-defined properties.
Adopting those constraints, the unknown parameters become: 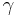 ,
, 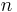 ,
, 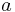 ,
, 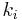 and
and 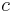 .
.
Determination of the model paremeters using experimental input and output data can be accomplished by system identification techniques. The procedures suggested in the literature include:
- Optimization based on the least-squares method, (using Gauss-Newton methods, evolutionary algorithms, genetic algorithms, etc.); in this case, the error difference between the time histories or between the short-time-Fourier transforms of the signals is minimized.
- Extended Kalman filter, unscented Kalman filter, particle filters
- Differential evolution
- Adaptive laws
Once an identification method has been applied to tune the Bouc-Wen model parameters, the resulting model is considered a good approximation of true hysteresis when the error between the experimental data and the output of the model is small enough (from a practical point of view).
References
- ^ Bouc, R. (1967). "Forced vibration of mechanical systems with hysteresis". Proceedings of the Fourth Conference on Nonlinear Oscillation. Prague, Czechoslovakia. pp. 315.
- ^ Bouc, R. (1971). "Modèle mathématique d'hystérésis: application aux systèmes à un degré de liberté" (in French). Acustica 24,: 16–25.
- ^ a b c Wen, Y. K. (1976). "Method for random vibration of hysteretic systems". Journal of Engineering Mechanics (American Society of Civil Engineers) 102 (2): 249–263.
- ^ a b J. Song and A. Der Kiureghian (2006) Generalized Bouc-Wen model for highly asymmetric hysteresis. Journal of Engineering Mechanics. ASCE. Vol 132, No. 6 p 610-618
- ^ a b F. Ma, H. Zhang, A. Bockstedte, G.C. Foliente and P. Paevere (2004). Parameter analysis of the differential model of hysteresis. Journal of applied mechanics ASME, 71, p. 342-349
- ^ a b T. T. Baber and Y. K. Wen (1981). Random vibrations of hysteretic degrading systems. Journal of Engineering Mechanics. ASCE. 107(EM6), p. 1069--1089
- ^ T. T. Baber and M. N. Noori (1985). Random vibration of degrading pinching systems. Journal of Engineering Mechanics. ASCE. 111 (8) p. 1010--1026 .
- ^ T. T. Baber and M. N. Noori (1986). Modeling general hysteresis behaviour and random vibration applications. Journal of Vibration, Acoustics, Stress, and Reliability in Design. 108 (4) p. 411--420
- ^ G. C. Foliente (1993). Stochastic dynamic response of wood structural systems. PhD dissertation. Virginial Polytechnic Institute and State University. Blacksburg, Virginia
- ^ a b C. P. Heine (2001). Simulated response of degrading hysteretic joints with slack behaviour. PhD dissertation. Virginial Polytechnic Institute and State University. Blacksburg, Virginia URL: http://scholar.lib.vt.edu/theses/available/etd-08092001-100756/
- ^ Y. J. Park, A. H. S. Ang and Y. K. Wen (1986). Random vibration of hysteretic systems under bi-directional ground motions. Earthquake Engineering Structural Dynamics, 14, 543--557
- ^ C. H. Wang and Y. K. Wen (1998) Reliability and redundancy of pre-Northridge low-rise steel building under seismic action. Rep No. UILU-ENG-99-2002, Univ. Illinous at Urbana-Champaign, Champaign, Ill.
- ^ F. Ihkouane and F. Pozo and L. Acho. Discussion of ``Generalized Bouc-Wen model for highly asymmetric hysteresis by Junho Song and Armen Der Kiureghian. Journal of Engineering Mechanics. ASCE. May 2008. p. 438--439
- ^ M. C. Constantinou and M. A. Adnane (1987). Dynamics of soil-base-isolated structure systems: evaluation of two models for yielding systems. Report to NSAF: Department of Civil Engineering, Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA
![\dot{z}(t) = \dot{u}(t) \left\{A - \left[\beta\operatorname{sign}(z(t)\dot{u}(t)) %2B \gamma \right]|z(t)|^n \right\}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/2ddbcd30d75f6bdfa7d18deb957408b3.png)
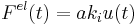
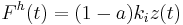
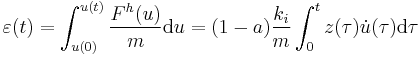
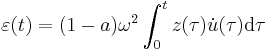
![\dot{z}(t) = \frac{h(z(t))}{\eta(\varepsilon)} \dot{u}(t) \left\{A(\varepsilon) - \nu(\varepsilon)\left[\beta\operatorname{sign}(\dot{u}(t))|z(t)|^{n-1} z(t) %2B \gamma |z(t)|^n \right] \right\}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/bc92e4cebd9b9928dcc00ec4f13c9ed3.png)
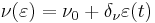
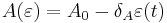
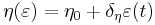
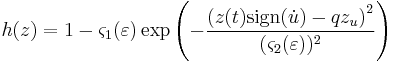
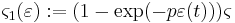
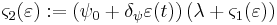
![z_u = \sqrt[n]{\frac{1}{\nu(\beta%2B\gamma)}}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/488e174a84fe9e262f3fcb282781c29a.png)
![\dot{z}(t) = \dot{u}(t) \left\{A - \left[\gamma %2B \beta\operatorname{sign}(z(t)\dot{u}(t)) %2B \phi(\operatorname{sign}(\dot{u}(t))%2B\operatorname{sign}(z(t))) \right]|z(t)|^n \right\}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/586781cd9cb731d94f75a75a8a152115.png)
![\dot{z}(t) = \dot{u}(t) \left\{A - \left[ \beta_1 \operatorname{sign}(\dot{u}(t)z(t)) %2B \beta_2 \operatorname{sign}(u(t)\dot{u}(t)) %2B \beta_3 \operatorname{sign}(u(t)z(t)) %2B \beta_4 \operatorname{sign}(\dot{u}(t)) %2B \beta_5 \operatorname{sign}(z(t)) %2B \beta_6 \operatorname{sign}(u(t)) %2B \right]|z(t)|^n \right\}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/21935e3a6bef98e7cb053152412dd9a3.png)
![\left[ \begin{array}{c} \dot{x}_1(t) \\ \dot{x}_2(t) \\ \dot{x}_3(t) \end{array} \right] = \left[ \begin{array}{c} x_2(t) \\ m^{-1} \left[ f(t) - c x_2(t) - a k_i x_1(t) - (1-a) k_i x_3(t)\right] \\ x_2(t) \left\{A - \left[\beta\operatorname{sign}(x_3(t)x_2(t)) %2B \gamma\right]|x_3(t)|^n \right\} \end{array} \right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/5df9a577bb2c7a561e2261e6c6a739be.png)
![\left[ \begin{array}{c} \dot{x}_1(t) \\ \dot{x}_2(t) \\ \dot{x}_3(t) \\ \dot{x}_4(t) \end{array} \right] =
\left[ \begin{array}{c} x_2(t) \\
m^{-1} \left[ f(t) - c x_2(t) - a k_i x_1(t) - (1-a) k_i x_3(t)\right] \\
\frac{h(x_3(t))}{\eta(x_4(t))} x_2(t) \left\{A(x_4(t)) - \nu(x_4(t))\left[\beta\operatorname{sign}(x_3(t)x_2(t)) %2B \gamma \right]|x_3(t)|^n \right\} \\
(1-a) \omega^2 x_3(t) x_2(t) \end{array} \right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/6b780e257e193fb72d7130f60ddc5ed1.png)